Bilingual Language Development and the Benefits of Bilingualism
Parents of children in multilingual homes often wonder how learning more
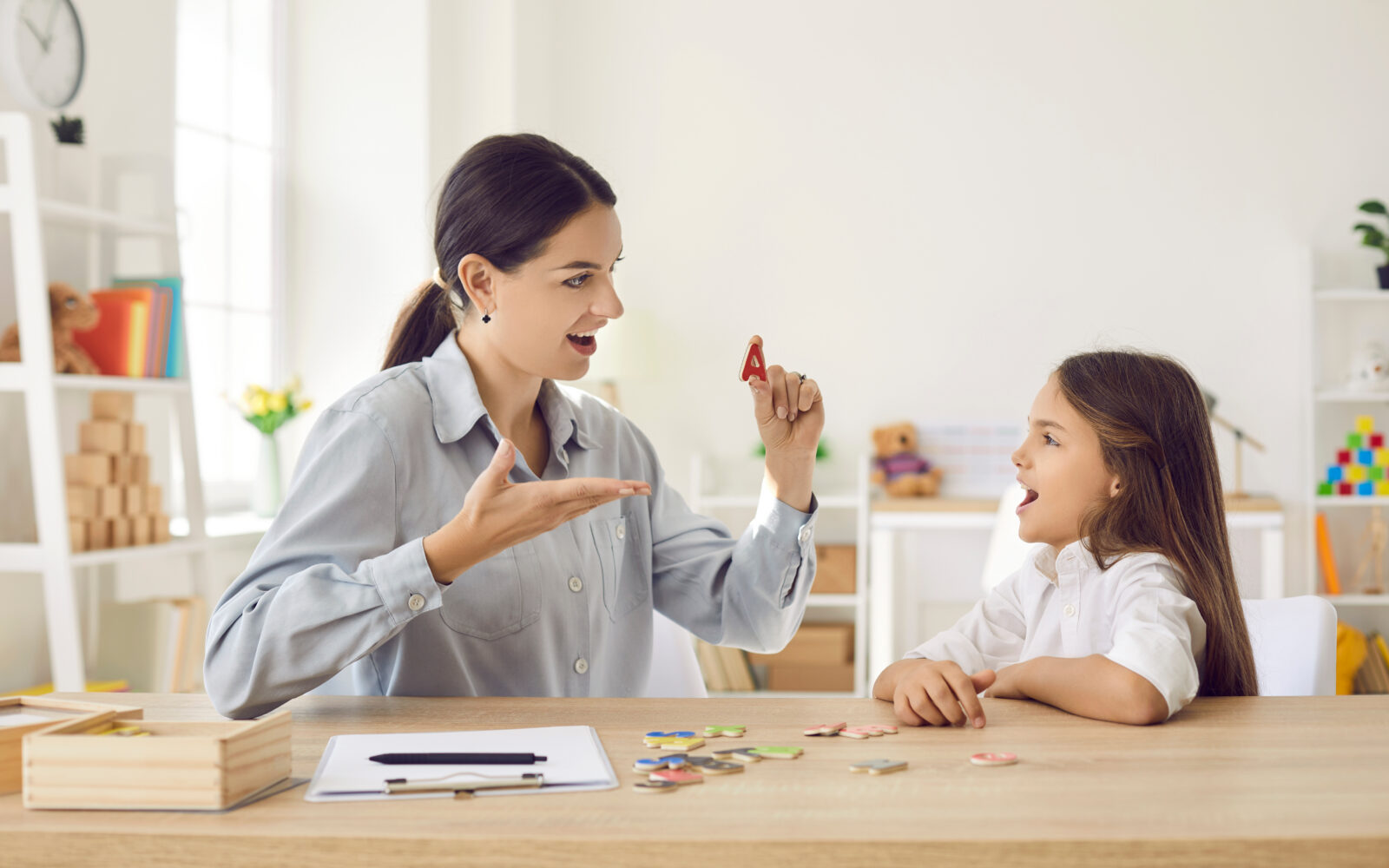

Parents of children in multilingual homes often wonder how learning more

As the weather shifts and the holiday season approaches, many of us look
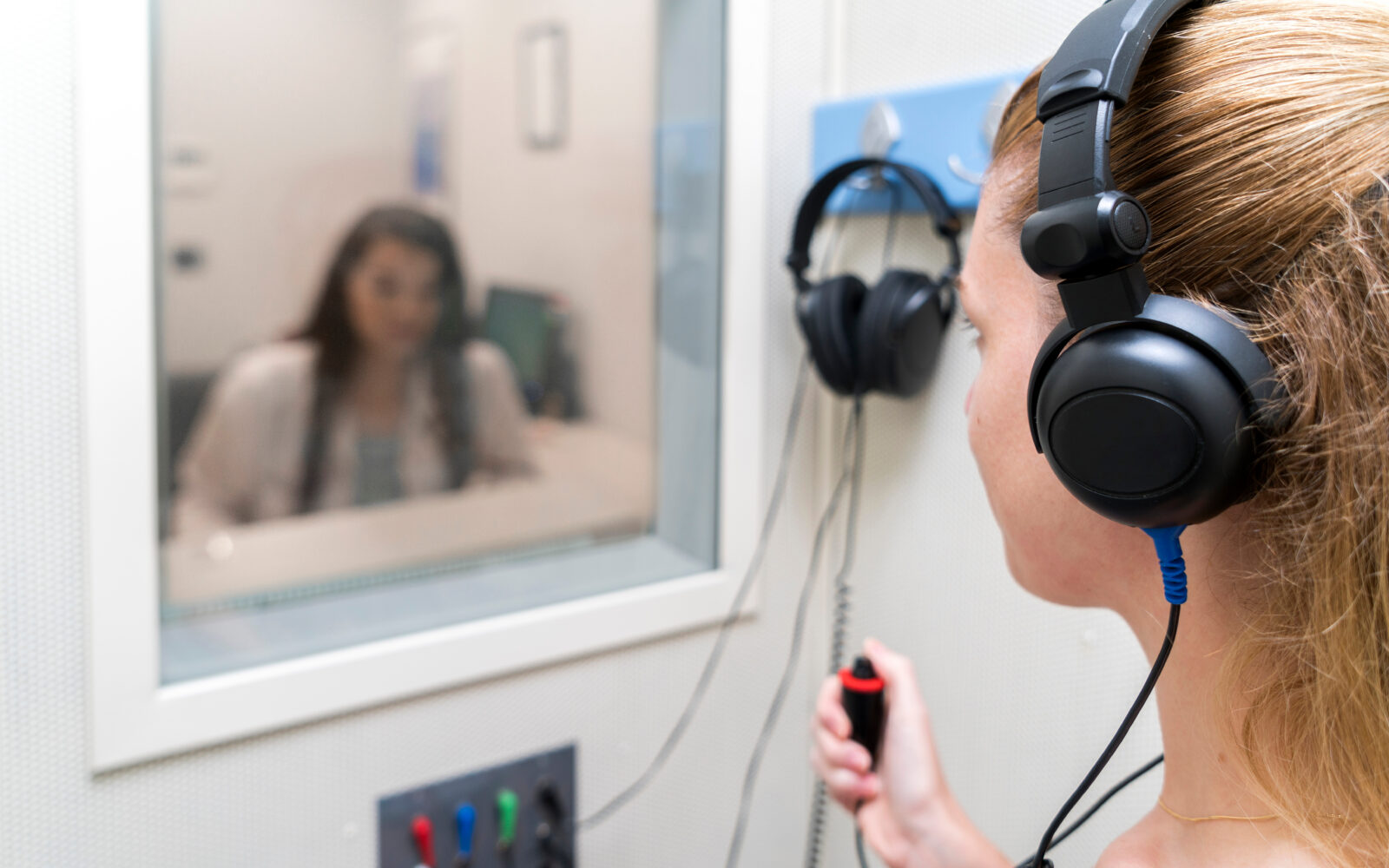

Hearing Aids Hearing Health Hearing Tests
Hearing loss often develops gradually, making it easy to ignore the early